- Головна
- Готові шкільні презентації
- Презентація на тему «Things that changed the world»
Презентація на тему «Things that changed the world»
168
Слайд #1
Things that changed the world
Tarasiyk MariaB-9-4
Tarasiyk MariaB-9-4

Слайд #2
Invention is the creation of a new device, process, or product. Inventions have given people enormous control over the environment and enabled to live better, easier, and happier lives. If people could not invent, they would be at the mercy of the climate and the land. Inventions have enabled people to survive the hazards of the environment and develop a civilized society.

Слайд #3
Invention is the creation of a new device, process, or product. Inventions have given people enormous control over the environment and enabled to live better, easier, and happier lives. If people could not invent, they would be at the mercy of the climate and the land. Inventions have enabled people to survive the hazards of the environment and develop a civilized society.

Слайд #4
Down through history, inventions have changed the way people live. Little by little, they have helped determine where people live and the kind of work they do. Inventions have also helped determine what people eat and wear and how they play and relax. Many thousands of years ago, people lived by hunting animals and gathering wild plants.

Слайд #5
To find food, people had to move from place to place. About 9000 B.C., people began to grow their own food and raise livestock. The invention of agriculture meant that people no longer had to wander about in search of food but could settle in farm villages. Then came the Industrial Revolution in the 1700's, with such inventions as spinning and weaving machines and the steam engine. These inventions produced another great change in the way people lived, as people flocked to the cities to work in factories.

Слайд #6
An invention differs from a discovery, but they are closely related. A discovery occurs when something that exists in nature is observed or recognized for the first time. An invention is the creation of something that never existed before. For example, people discovered fire. But they invented the match to start a fire.

Слайд #7
Invention is also related to innovation. Innovation is a change made in an established way of doing something. An innovation can make an invention more accessible to people, thereby increasing the use of invention. Henry Ford, who founded the Ford Motor Company, was an outstanding innovator. Ford did not invent the automobile, but he brought several innovations to the manufacture of automobiles. These innovations included assembly line method of production, and having the company make, rather than buy, automobile parts. Ford's innovations enabled the company to slash the price of its automobiles, putting them within reach of the average family.

Слайд #8
Although most inventions have benefited people, some inventions, such as weapons of war, have been harmful. Certain other inventions have been both beneficial and harmful. The automobile, for example, has given us a fast, convenient means of transportation. However, it has also contributed greatly to air pollution.

Слайд #9
Air pollution is only one of the many problems that people face today. Large numbers of cities are overcrowded. More than half the world's people do not have enough to eat. Heart disease and other illnesses kill countless millions every year. To solve these and other problems, people must rely largely on their ability to invent.

Слайд #10
Circle the letter of the best answer:
1. Invention is
the observation of something new.
the investigation of nature.
the creation of a new device, process, or product.
2. Discovery is
observation or recognition of something that exists.
the creation of something that never existed.
a new way to do something.
3. Innovation is
the process of observation.
the creation of something unusual.
a change made in an established way of doing something.
1. Invention is
the observation of something new.
the investigation of nature.
the creation of a new device, process, or product.
2. Discovery is
observation or recognition of something that exists.
the creation of something that never existed.
a new way to do something.
3. Innovation is
the process of observation.
the creation of something unusual.
a change made in an established way of doing something.

Слайд #11
I. Circle T if the statement is true. Circle F if the statement is false:
Inventions make life better, easier and happier.
People invented fire.
Invention is related to innovation.
Inventions were of great importance for development of a civilized society.
Henry Ford invented automobile.
Most inventions have benefited people.
The ability to invent is of no help to solve the problems people face today.
Innovations make productions more expensive.
An innovation makes an invention more accessible to people.
Some inventions may be both harmful and beneficial.
Inventions make life better, easier and happier.
People invented fire.
Invention is related to innovation.
Inventions were of great importance for development of a civilized society.
Henry Ford invented automobile.
Most inventions have benefited people.
The ability to invent is of no help to solve the problems people face today.
Innovations make productions more expensive.
An innovation makes an invention more accessible to people.
Some inventions may be both harmful and beneficial.

Слайд #12
Telephone
The telephone was invented by British inventor Alexander Graham Bell and patented in 1876. Bell left school at age 15, but maintained a keen interest in science and biology. Moving to London to live with his grandfather, Bell developed a love for learning and spent hours each day in study. Aged 16, he went to teach elocution and music at Weston House Academy in Moray, Scotland. A year later, Bell attended the University of Edinburgh, later being accepted into the University of London. His early experiments with sound began when he was taken to see a “speaking” automaton designed by Baron Wolfgang von Kempelen and built by Sir Charles Wheatstone.
Alexander Graham Bell
1847-1922
The telephone was invented by British inventor Alexander Graham Bell and patented in 1876. Bell left school at age 15, but maintained a keen interest in science and biology. Moving to London to live with his grandfather, Bell developed a love for learning and spent hours each day in study. Aged 16, he went to teach elocution and music at Weston House Academy in Moray, Scotland. A year later, Bell attended the University of Edinburgh, later being accepted into the University of London. His early experiments with sound began when he was taken to see a “speaking” automaton designed by Baron Wolfgang von Kempelen and built by Sir Charles Wheatstone.
Alexander Graham Bell
1847-1922

Слайд #13
Fascinated by the machine, Bell purchased a copy of a book written in German by Baron Wolfgang von Kempelen and built a similar automaton with his brother. Many years later, while working at Boston University School of Oratory, Bell became interested in technology to transmit sound. Leaving his job a the university, he made the decision to pursue his personal research on the subject. In 1875, Bell created an acoustic telegraph which he patented in March 1876 following a close race with American inventor Elisha Gray, who accused Graham Bell of stealing the invention from him. The patent office ultimately ruled in Bell's favor and he was granted the patent for the world's first telephone.

Слайд #14
Theory of Evolution
Charles Darwin
1809-1882
Charles Darwin was a British naturalist born in 1809. Darwin was the first person to propose the now popular theories of evolution, natural selection and common descent. After a 5 year voyage around the globe aboard the HMS Beagle, Darwin returned to Britain finding himself a celebrity in scientific circles following distribution of his letters to various scientists at home while he had been away studying geology aboard the Beagle. Darwin went on to be elected to the Council of the Geological Society, later moving to London to continue his work and join a circle of scientists which included Charles Babbage.
Charles Darwin
1809-1882
Charles Darwin was a British naturalist born in 1809. Darwin was the first person to propose the now popular theories of evolution, natural selection and common descent. After a 5 year voyage around the globe aboard the HMS Beagle, Darwin returned to Britain finding himself a celebrity in scientific circles following distribution of his letters to various scientists at home while he had been away studying geology aboard the Beagle. Darwin went on to be elected to the Council of the Geological Society, later moving to London to continue his work and join a circle of scientists which included Charles Babbage.

Слайд #15
Darwin formed his theory of evolution over much of his life, only publishing it in his later years in his book “On The Origin of Species” for fear of how the public would respond to what was, at the time, a highly controversial theory, since it proposed a means by which life developed on Earth without a God. Charles Darwin continued, despite controversy (and in some cases ridicule), his work until his death on 19th April 1882 from heart disease, likely brought on from years of illness, overwork and stress.

Слайд #16
Steam Locomotive
The first steam locomotive was invented by Richard Trevithick, a British inventor and mining engineer. Trevithick's steam locomotive was built in 1804 in Pen-y-Darren in South Wales to carrying cargo. Trevithick sold the patents to the steam locomotive to Samuel Homfray. In one of the earliest public demonstrations, the locomotive successfully carried an impressive load of 10 tons of iron, 5 wagons and 70 men 9.75 miles between Penydarren and Abercynon in 4 hours and 5 minutes. Trevithick continued to work with steam locomotives for many more years until his death in April 1833.
Richard Trevithick
1771-1833
The first steam locomotive was invented by Richard Trevithick, a British inventor and mining engineer. Trevithick's steam locomotive was built in 1804 in Pen-y-Darren in South Wales to carrying cargo. Trevithick sold the patents to the steam locomotive to Samuel Homfray. In one of the earliest public demonstrations, the locomotive successfully carried an impressive load of 10 tons of iron, 5 wagons and 70 men 9.75 miles between Penydarren and Abercynon in 4 hours and 5 minutes. Trevithick continued to work with steam locomotives for many more years until his death in April 1833.
Richard Trevithick
1771-1833

Слайд #17
A full-scale working replica of his first steam locomotive was built in 1981 for the Welsh Industrial and Maritime Museum, later moving to the National Waterfront Museum in Swansea. The locomotive is run several times a year along a short length of rail outside the museum.

Слайд #18
Television
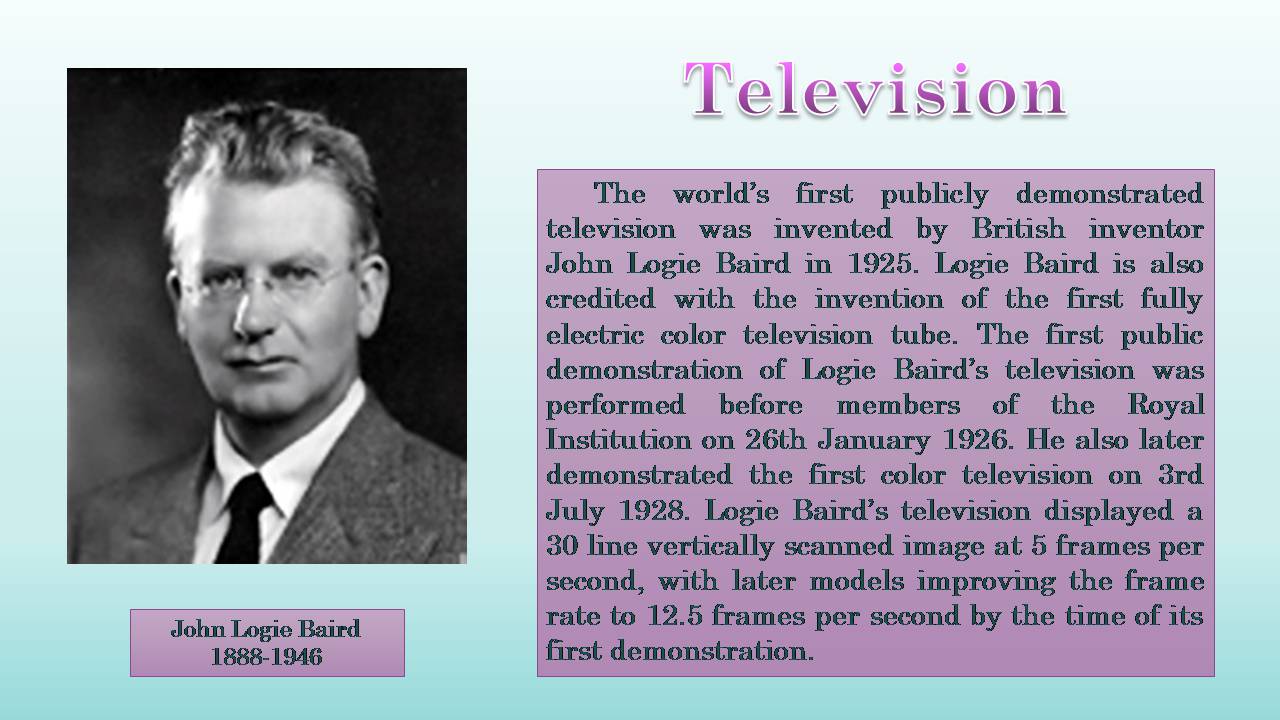
The world's first publicly demonstrated television was invented by British inventor John Logie Baird in 1925. Logie Baird is also credited with the invention of the first fully electric color television tube. The first public demonstration of Logie Baird's television was performed before members of the Royal Institution on 26th January 1926. He also later demonstrated the first color television on 3rd July 1928. Logie Baird's television displayed a 30 line vertically scanned image at 5 frames per second, with later models improving the frame rate to 12.5 frames per second by the time of its first demonstration.
John Logie Baird
1888-1946
The world's first publicly demonstrated television was invented by British inventor John Logie Baird in 1925. Logie Baird is also credited with the invention of the first fully electric color television tube. The first public demonstration of Logie Baird's television was performed before members of the Royal Institution on 26th January 1926. He also later demonstrated the first color television on 3rd July 1928. Logie Baird's television displayed a 30 line vertically scanned image at 5 frames per second, with later models improving the frame rate to 12.5 frames per second by the time of its first demonstration.
John Logie Baird
1888-1946
Слайд #19
Logie Baird's invention paved the way for what is now nearly a century of work on the development of television technology, which remains one of the most influential inventions in history, allowing people all over the world to communicate via moving images.

Слайд #20
World Wide Web
Not to be confused with the Internet (a global system of networked computers invented in the USA), the World Wide Web, invented by British computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee, is the system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet. The World Wide Web is most commonly experienced as the system behind the concept of web pages and websites. Berners-Lee first proposed the concept of the World Wide Web in March 1989, later pitching it at CERN along with Belgian scientist Robert Cailliau. CERN then publicly introduced the project in December of 1990.
Tim Berners-Lee
b. 1955
Not to be confused with the Internet (a global system of networked computers invented in the USA), the World Wide Web, invented by British computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee, is the system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet. The World Wide Web is most commonly experienced as the system behind the concept of web pages and websites. Berners-Lee first proposed the concept of the World Wide Web in March 1989, later pitching it at CERN along with Belgian scientist Robert Cailliau. CERN then publicly introduced the project in December of 1990.
Tim Berners-Lee
b. 1955

Слайд #21
The first website, info.cern.ch, went live at CERN on 6th August 1991. Interestingly, Berners-Lee, although realizing the potential for immense personal profit from his invention, chose instead to gift the idea to the world, requesting no payment.
The Web's logo designed by Robert Cailliau
The Web's logo designed by Robert Cailliau

Слайд #22
Programmable Computer
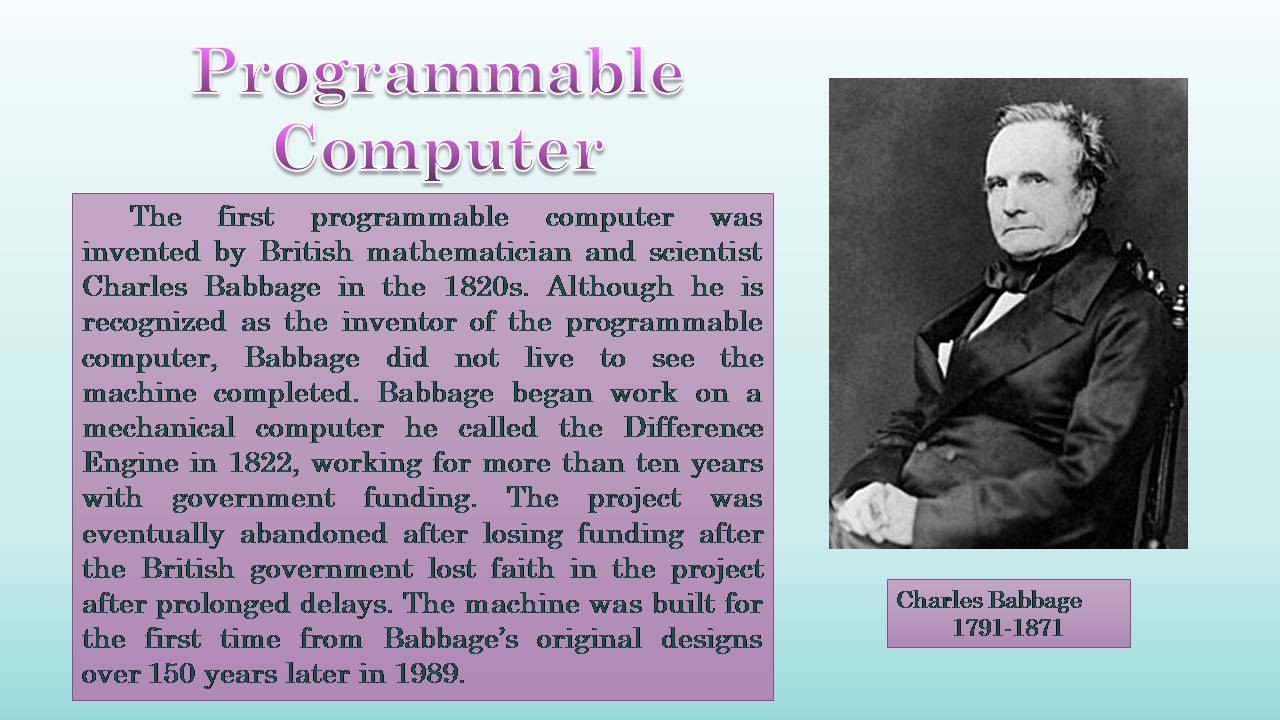
The first programmable computer was invented by British mathematician and scientist Charles Babbage in the 1820s. Although he is recognized as the inventor of the programmable computer, Babbage did not live to see the machine completed. Babbage began work on a mechanical computer he called the Difference Engine in 1822, working for more than ten years with government funding. The project was eventually abandoned after losing funding after the British government lost faith in the project after prolonged delays. The machine was built for the first time from Babbage's original designs over 150 years later in 1989.
Charles Babbage
1791-1871
The first programmable computer was invented by British mathematician and scientist Charles Babbage in the 1820s. Although he is recognized as the inventor of the programmable computer, Babbage did not live to see the machine completed. Babbage began work on a mechanical computer he called the Difference Engine in 1822, working for more than ten years with government funding. The project was eventually abandoned after losing funding after the British government lost faith in the project after prolonged delays. The machine was built for the first time from Babbage's original designs over 150 years later in 1989.
Charles Babbage
1791-1871
Слайд #23
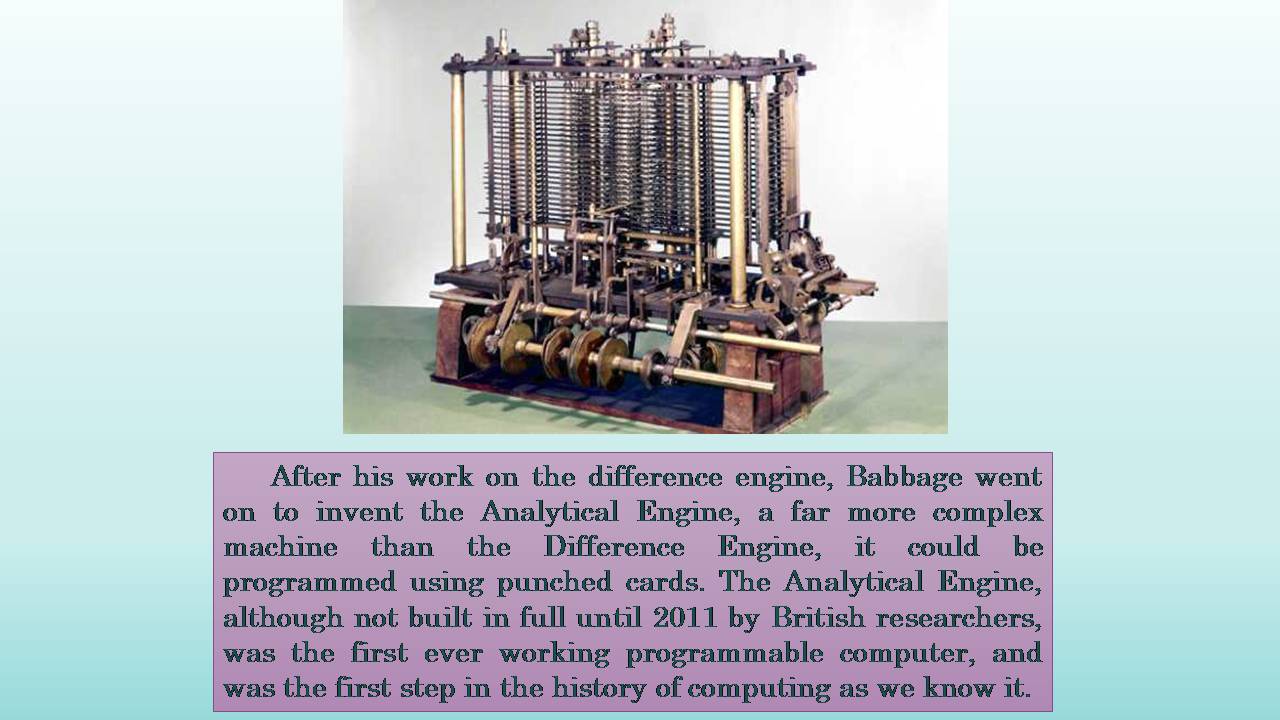
After his work on the difference engine, Babbage went on to invent the Analytical Engine, a far more complex machine than the Difference Engine, it could be programmed using punched cards. The Analytical Engine, although not built in full until 2011 by British researchers, was the first ever working programmable computer, and was the first step in the history of computing as we know it.
Слайд #24
Newton's Laws
Isaac Newton was a British physicist and mathematician. Born in 1642, Newton discovered and documented for the first time three laws of motion in regard to physics. Newton's Laws are as follows – 1st Law: An object at rest tends to stay at rest unless acted upon by an external force and an object in uniform motion tends to remain in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. 2nd Law: An applied force on an object equals the rate of change of its momentum. 3rd Law: Every action has an equal and opposite reaction. Newton was also the first person to document the mechanics of universal gravitation. Newton's work is some of the most influential in the history of modern science, many regarding him to be one of the most important scientists in human history.
Isaac Newton
1642-1727
Isaac Newton was a British physicist and mathematician. Born in 1642, Newton discovered and documented for the first time three laws of motion in regard to physics. Newton's Laws are as follows – 1st Law: An object at rest tends to stay at rest unless acted upon by an external force and an object in uniform motion tends to remain in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. 2nd Law: An applied force on an object equals the rate of change of its momentum. 3rd Law: Every action has an equal and opposite reaction. Newton was also the first person to document the mechanics of universal gravitation. Newton's work is some of the most influential in the history of modern science, many regarding him to be one of the most important scientists in human history.
Isaac Newton
1642-1727

Слайд #25
Nearly Every Modern Sport
Most popular sports in the modern world trace their history to Britain, at least in terms of standardization of the rulesets and widespread competitive play. The most notable being Football, Cricket, Rugby and Tennis. Many other modern sports trace their history to variations on British sports, such as American Football (derived from Rugby) and Baseball (derived from Rounders). Of course, the British weren't the first to think of kicking a ball around in a field, but the British standardized the structure and rules of most modern competitive sports as we know them today.
Most popular sports in the modern world trace their history to Britain, at least in terms of standardization of the rulesets and widespread competitive play. The most notable being Football, Cricket, Rugby and Tennis. Many other modern sports trace their history to variations on British sports, such as American Football (derived from Rugby) and Baseball (derived from Rounders). Of course, the British weren't the first to think of kicking a ball around in a field, but the British standardized the structure and rules of most modern competitive sports as we know them today.

Слайд #26
WRITING
Since time immemorial mankind has sought ways to transfer information. Primitive people used scrap materials: somehow constituted branch signals are passed through the smoke of bonfires and more. But a breakthrough in human development was possible only with the advent of letters about 4 thousand years BC
Since time immemorial mankind has sought ways to transfer information. Primitive people used scrap materials: somehow constituted branch signals are passed through the smoke of bonfires and more. But a breakthrough in human development was possible only with the advent of letters about 4 thousand years BC

Слайд #27
TYPOGRAPHY
How typography meet urgent human needs, showed the very first years after the invention of Gutenberg in the mid XV century. The appearance of books contributed easier information transfer. This sparked the green light to the Renaissance.
How typography meet urgent human needs, showed the very first years after the invention of Gutenberg in the mid XV century. The appearance of books contributed easier information transfer. This sparked the green light to the Renaissance.
Слайд #28
TELEGRAPH
Until the mid-XIX century events and developments in other countries, people learned late for weeks and sometimes for months. The only way to transfer information over long distances was shipping mail. Meanwhile, the need for rapid communication increase. Therefore, the invention of the telegraph was the best discovery of the day. In 1832, during his trip to America created a model Morse telegraph and Morse famous.
Until the mid-XIX century events and developments in other countries, people learned late for weeks and sometimes for months. The only way to transfer information over long distances was shipping mail. Meanwhile, the need for rapid communication increase. Therefore, the invention of the telegraph was the best discovery of the day. In 1832, during his trip to America created a model Morse telegraph and Morse famous.

Слайд #29
At the end of XIX century, mankind has continued to seek new ways of rapprochement. It should been more perfect than a telegraph, a tool that would be accessible to all.
And after several years of hard work the first phone Bella "talking". March 10, 1876 his assistant Watson clearly heard at the receiving station Bell's words, "Mr. Watson, please come here, I need to talk to you." Bell patented his invention, and in August of that in 1876 there were already in use about 800 phones. Demand for them, of course, quickly grew.
PHONE
And after several years of hard work the first phone Bella "talking". March 10, 1876 his assistant Watson clearly heard at the receiving station Bell's words, "Mr. Watson, please come here, I need to talk to you." Bell patented his invention, and in August of that in 1876 there were already in use about 800 phones. Demand for them, of course, quickly grew.
PHONE

Слайд #30
PHOTOGRAPHY & FILM
Equally important finding for civilization seemed to transfer images. In 1826, Joseph Niepce using the pinhole camera was on a metal plate view from the window of his studio. And in 1837, Louis Jacques Mande Daguerre first got shot with a relatively high image quality.
In 1891, the tireless inventor Tom Edison invented the peep show - serial device to demonstrate the effect of motion pictures. This invention inspired by the Lumiere brothers to create a movie. In December 1895, in Paris, on the Boulevard des Capucines, the first performance. Spectators witnessed a miracle - a white screen changed each other real moving pictures. In these mass pictures taken a huge emotional impact.
Equally important finding for civilization seemed to transfer images. In 1826, Joseph Niepce using the pinhole camera was on a metal plate view from the window of his studio. And in 1837, Louis Jacques Mande Daguerre first got shot with a relatively high image quality.
In 1891, the tireless inventor Tom Edison invented the peep show - serial device to demonstrate the effect of motion pictures. This invention inspired by the Lumiere brothers to create a movie. In December 1895, in Paris, on the Boulevard des Capucines, the first performance. Spectators witnessed a miracle - a white screen changed each other real moving pictures. In these mass pictures taken a huge emotional impact.

Слайд #31
RADIO
Thought inventors did not stop transmission by wire. Popov was looking for a new way of rapprochement between people and found it. In 1895. He demonstrated wireless telegraphy apparatus. And in 1899, Italian inventor Marconi made radio transmission across the Channel, and in 1901 - across the Atlantic. In 1904 the English scientist J. E.Fleminh improved radiotelegraph receiver, and in 1913 the German A. Meissner created the first radiotelephone transmitter.
Thought inventors did not stop transmission by wire. Popov was looking for a new way of rapprochement between people and found it. In 1895. He demonstrated wireless telegraphy apparatus. And in 1899, Italian inventor Marconi made radio transmission across the Channel, and in 1901 - across the Atlantic. In 1904 the English scientist J. E.Fleminh improved radiotelegraph receiver, and in 1913 the German A. Meissner created the first radiotelephone transmitter.

Слайд #32
TV
One of the most remarkable inventions of XX century television. Like other complex technical solutions, television appeared and developed through the efforts of many inventors.
In 1911, professor of St. Petersburg University of Technology B. Rosing demonstrated the world's first image on the glass screen cathode-ray tube.
In 1928, the inventor Boris Grabowski found a way to transfer a moving image on the distance. And in 1929, the U.S. Vladimir Zworykin developed High reception cathode-ray tube called the kinescope them. Later she and her modifications used in all TVs.
One of the most remarkable inventions of XX century television. Like other complex technical solutions, television appeared and developed through the efforts of many inventors.
In 1911, professor of St. Petersburg University of Technology B. Rosing demonstrated the world's first image on the glass screen cathode-ray tube.
In 1928, the inventor Boris Grabowski found a way to transfer a moving image on the distance. And in 1929, the U.S. Vladimir Zworykin developed High reception cathode-ray tube called the kinescope them. Later she and her modifications used in all TVs.

Слайд #33
PC
The emergence of computer summed up all the semantic inventions last century. He became the primary means of processing and storing information with possible transfer to any distance. But the main thing - it is extremely computer expanded our capacity for creativity.
The emergence of computer summed up all the semantic inventions last century. He became the primary means of processing and storing information with possible transfer to any distance. But the main thing - it is extremely computer expanded our capacity for creativity.

Слайд #34
INTERNET
Tenth invention that changed the world, was the most revolutionary. In 1989, Berners-Lee proposed a fantastic project relationship, now known as the World Wide Web, bringing together today for the quarter of the world's population (or 1.4 billion people).
Why the Internet was a landmark invention? Internet has made the world a small village, where information spreads "the speed of sound." But most importantly - Internet unthinkable reduced distance. For monitor screen appears virtual reality, where our capabilities are not limited by time and space.
Tenth invention that changed the world, was the most revolutionary. In 1989, Berners-Lee proposed a fantastic project relationship, now known as the World Wide Web, bringing together today for the quarter of the world's population (or 1.4 billion people).
Why the Internet was a landmark invention? Internet has made the world a small village, where information spreads "the speed of sound." But most importantly - Internet unthinkable reduced distance. For monitor screen appears virtual reality, where our capabilities are not limited by time and space.

Слайд #35
Thank you for your attention!
